I was Hawai‘i County’s representative to the 2011 Association for the Study of Peak Oil conference in Washington, D.C., which just concluded.
This was the fourth time I’ve attended the conference. After my first ASPO conference it hit me: I learned too much! It became my kuleana.
This is the third in a series of posts about information gleaned from this year’s conference. Note that everything I’m writing about is based on numbers, not my opinions. I am relaying information from very credible people who have gone through the peer review process and been vetted.
Energy Return on Energy invested (EROI or EROEI)
In a sentence, the definition of EROI: “The energy it takes to get energy – minus the energy it takes to get food – equals our lifestyle.”
Charles Hall, David Murphy and others, who have done peer-reviewed analyses of the concept of EROI, argue that organisms, organizations and civilizations must generate surplus energy in order to survive. A mother cheetah must be able to chase down rabbits and gazelles, miss a few, feed the kids and still have enough energy to run down more or else the species goes extinct. Ancient civilizations followed this principle.
This is Charley Hall, the father of EROI, on the left.

Awhile ago, I read through his paper “What is the Minimum EROI that a Sustainable Society Must Have?, which he authored with Stephen Balogh and David Murphy, and I immediately got it. At the conference, I asked Charley to autograph a copy of it for me.
I was sitting right next to him and asked him how come there are no analyses for “hot” geothermal, like we have in Hawai‘i and Iceland. His answer was that we are a tiny part of the world solution. I guess so – we are only 2 million out of 7 billion people that are so lucky.
If it takes more energy to get the energy (as in some biofuels), then someone needs to explain to regular folks why we would do that. Otherwise, we start thinking about Easter Island.
Can we pay back our debts if the economy cannot grow? It is clear that the economy cannot stand a triple digit oil price. We have been using twice as much oil as we have been finding for more than 20 years now.
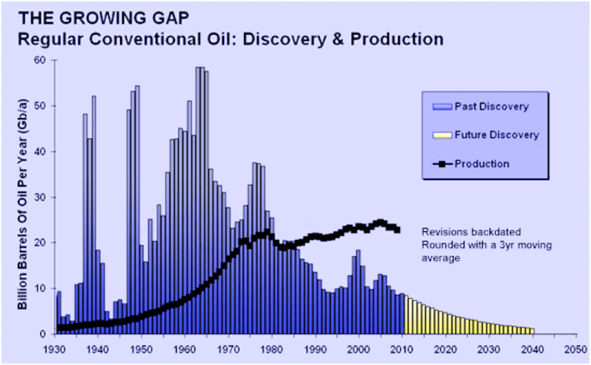
And it is becoming more difficult and, consequently, more expensive to develop new sources. It seems reasonable to assume that oil prices will rise and fall with demand. But the prices will tend to keep rising as the population’s demand rises and as old fields naturally decline.
And doesn’t modern economic theory assume continuous growth? But growth stops when oil reaches triple digits per barrel. Are we facing the end of growth? It is prudent that we plan for the worse and hope for the best.
Both Gail Tverberg and Jeff Rubin write blogs about this (both their blogs are always available by clicking in the side bar at right).
Here I am with Gail. I cannot refute her arguments, so I spend all my time figuring out workarounds. That’s why I push geothermal so hard. It’s the bridge that will enables other renewables to cross.

Hawaii Pacific University (HPU) in Honolulu is sponsoring a talk about the end of growth by Richard Heinberg on November 9th. Heinberg is a Senior Fellow-in-Residence at Post Carbon Institute, a nonprofit organization dedicated to “building more resilient, sustainable, and equitable communities.”
This is Richard Heinberg on the left.

This series of posts about my trip to the 2011 Association for the Study of Peak Oil (ASPO) continues. Read Part 4 here.
Go back to Part 1 and Part 2.




