In November, I will attend my fourth Association for the Study of Peak Oil (ASPO) conference.
I highly recommend that Hawai‘i people in decision-making positions attend.
This year’s conference theme is “Truth In Energy,” and it will focus on the importance of transparent and reliable energy information, and the need to educate influential leaders and the public on the peak oil energy challenges facing our nation.
Energy is a very complex subject, and it’s sometimes difficult to separate the truth from the marketing hype. The value I get from attending these conferences is in being able to determine the difference between the middle ground, the fringe, the hopesters and the hypesters.
For example, when I went to my first ASPO conference in Houston, a speaker pointed out that the peak of oil production in the U.S. occurred in 1970. Although Saudi Arabia keeps their oil reserve data secret, there are ways that regular folks can make reasonable assumptions. He said that there were people from Saudi Arabia working in the oil industry in Houston, and that they had learned how to not waste their resource.
On April 13, 2008, Reuters reported that King Abdullah said, “When there were some new finds, I told them, ‘No, leave it in the ground, with grace from God, our children need it.’”
That was not reported in the mainstream media, but because I went to the ASPO conference, I read about it. I heard the King very clearly.
There are also others who, through regular means like Google Earth, make reasonable assumptions.
Take a look at this animation and narrative about Saudi oil fields. It seems reasonable to assume that the Saudis cannot keep on pumping endlessly.
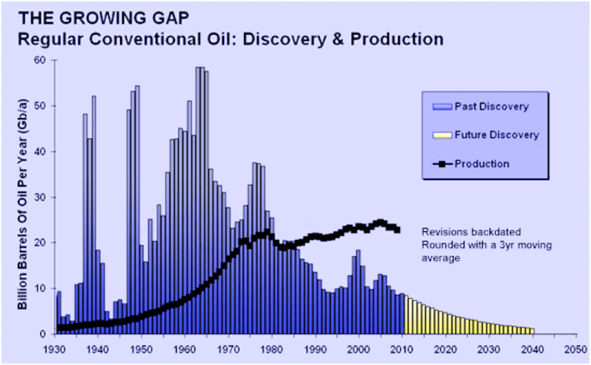
Any “rubbah slippah” person can understand that this shows more and more oil being sucked out of the ground, and it will begin to decline. It’s all about supply and demand, and because oil is a finite resource, we should expect rising oil prices.
At the 2009 conference in Denver, someone showed a graph that pointed out the direct relationship between oil price, GDP and the last several recessions. The data showed that when oil prices exceeded $85 dollars or so, we could expect a recession.
The worrisome part is that hardly anyone makes the oil cost/recession connection. If they did, they would realize that unless we in Hawai‘i find a way to avoid the rising cost of fuel and electricity, we are at best looking at a future of very little economic growth. Because we are more reliant on oil than most, our future could be very bleak.
That is why we, in Hawai‘i, must force the change and go to low and stable cost geothermal faster, rather than slower. This will allow us to dodge the oil bullet, and will give us the opportunity to unleash the abundance of renewable energy alternatives available to us.
I really returned from a study trip to Iceland and learned that by using cheap geothermal and hydroelectric, that country is now food and fuel secure.
I am noticing more and more homeless people here. Many of them are working homeless. As we bring on more low-cost, stable geothermal, our standard of living and economic activity will rise. More and more of the working homeless will be able to get their families off the street. We can do this without having to tax the people.
We must force the change, but we will need everyone’s help. We are all in this together.
Dr. Charles Schlumberger, who is in charge of the airline section of the World Bank, spoke at the last ASPO conference. Watch video of his talk The Future of Air Transportation.
Jeff Rubin, former Chief Economist for the Canadian bank CIBC, spoke too, explaining how the world economy will shrink as oil prices rise. Here is his Oil and the End of Globalization speech.
This has very strong implications for Hawai‘i. We all know that we must get off oil. But the problem is the cost and practicality of the solution. Solutions need to be cost-effective and proven technology, as well as environmentally friendly.
Geothermal fits this requirement. But we need to move much faster than we have been.
When I return from this year’s conference, I will post this year’s speeches.