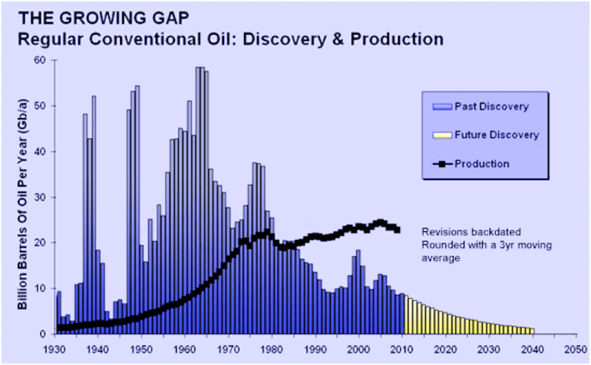
When I attended the Association for the Study of Peak Oil and Gas (ASPO USA) Conference in Washington, D.C. last week, I happened to be sitting next to the reporter for Platts News Service, Leslie Moore Mira.
Here are two reports she wrote about the conference, which sum things up well:
Peak oil panel debates severity, timing of potential crisis
Washington (Platts)–7Oct2010/553 pm EDT/2153 GMT
A panel of geologists and energy analysts debated Thursday the severity and timing of an anticipated oil crisis, with one saying during a Washington briefing that crude oil production has now peaked.
“The global rate of production of oil is peaking now,” said Tad Patzek, professor and chairman of the department of petroleum engineering at the University of Texas-Austin. “The size of accumulation [of oil] is not equated to the rate of production,” he said.
Frank Rusco, an energy director at the US Government Accountability Office, estimated some 45 years of “proven reserves,” though current and future oil demand will stress supplies.
“Higher oil prices can retard economic growth and even cause a recession in the right circumstance,” Rusco said at the briefing, which was organized by the Association for the Study of Peak Oil & Gas. He declined to say after the briefing what a gasoline price ceiling might be for US consumers.
“The remaining hydrocarbons will be more costly to get from underground,” from a “policy perspective,” Rusco said, citing the Middle East as a “fairly unstable” region.
Robert Hirsch, an energy adviser at MISI and former manager of Exxon’s synthetic fuels research laboratory, put the state of looming shortages in more dire terms, saying “in the next two to five years oil shortages will get deeper and deeper.”
Meanwhile “mitigation” of oil dependency by transitioning into other energy sources will take upward of a decade to come into play.
“Some time after a decade, mitigation will take impact and things will start to flatten out,” Hirsch said.
GHAWAR COULD MORPH INTO A CANTARELL: PROFESSOR
New reserves from Brazil and production from unconventional sources in the US will not be enough to compensate for depleting reserves, panelists said.
The Ghawar oil field in Saudi Arabia, still a bright light in the
petroleum world, could see a sharp and imminent decline in production, Patzek said.
If Ghawar “peters out, to replace it [with production elsewhere] will be a very difficult task,” he added. He estimated Ghawar’s current production at between 4.5 million-5 million b/d, though added that actual production figures are unknown as they are a “top secret.”
Later on the sidelines, Patzek said Ghawar could become the region’s Cantarell, referring to Mexico’s offshore oil field that has seen production plummet by over half from a peak 2.1 million b/d in the mid-2000s.
Patzek said that the ongoing water-flood efforts into the Ghawar field to stimulate production will eventually taper off. “You’re injecting twice as much water into the well,” he said. “Your field is watering out,” Patzek said in an interview.
Patzek told the briefing that that Norway’s reserves have peaked, while he characterized the decline rate in the US Gulf of Mexico as “very high.” BP’s Thunder Horse well in the Gulf “has not reached its potential and it’s declining faster than people thought,” Patzek said.
A BP spokesman was not immediately available for comment on Patzek’s remarks about Thunder Horse.
– Leslie Moore Mira, leslie_moore@platts.com
Collapse then surge predicted for oil prices at peak oil meeting
Washington( Platts)–11Oct2010/415 am EDT/815 GMT
A looming collapse in credit markets and liquidity could lead to wildly gyrating prices for crude oil within the next five years, with prices falling to $20/barrel, then possibly rocketing to $500/b, a peak oil theorist and commentator told the Association for the Study of Peak Oil and Gas conference.
“This is not a recovery that we’re in,” said Nicole Foss, a former fellow at the Oxford Institute for Energy Studies, who predicted “chaos” in foreign currency and equity markets within years. A severe deflationary plunge will contribute to a liquidity crisis among the financial sector, Foss said on a peak oil panel late last week. The meeting in Washington wrapped up Saturday.
“Oil will bottom early in this depression,” Foss said. She and fellow
panelist, energy analyst Chris Martenson, predicted that foreign currency markets will become more volatile, with domino effects on global money supply.
“It’s not unthinkable that the US will have another financial crisis,”
Martenson said, adding that he gave the US a “50%” shot at having a fiscal crisis and a “50%” chance of experiencing a currency crisis. “We’re going to see severe dislocations in the foreign exchange markets.”
“Deflation is tomorrow’s problem,” Foss said, adding that a lack of
purchasing power will undermine price support for crude oil. Then “printing [money] is a few years off,” she said. “We could see $20/barrel and then $500/barrel within the space of five years,” Foss said.
Foss runs the Agri-Energy Producers’ Association of Ontario, where she has focused on farm-based biogas projects and grid connections for renewable energy. At Oxford, she researched electricity policy at the EU level, according to her website. She was previously editor of the Oil Drum Canada, where she wrote about peak oil and finance.
Speaking on the sidelines of the conference, Foss said that natural gas holds no promise as a safe hydrocarbon haven in a scenario of volatile crude oil prices. There is a “perception of a glut” of natural gas reserves and other resources from new shale plays and coalbed methane, and tight formation gas, Foss said.
“I would argue that this is an illusion,” Foss said. The environmental cost of extracting unconventional resources “is tremendous,” Foss said, adding that the energy resource “bang for buck” is unappealing. “We’ll end up with natural gas price spikes,” after years of low natural gas prices, she said.
As a side event to the meeting, a panel of geologists and energy analysts debated at a Congressional briefing the severity and timing of what they believe will be an oil crisis, with one saying crude oil production has now peaked.
“The global rate of production of oil is peaking now,” said Tad Patzek,professor and chairman of the department of petroleum engineering at theUniversity of Texas-Austin. “The size of accumulation (of oil) is not equatedto the rate of production.”
Frank Rusco, an energy director at the US Government AccountabilityOffice, estimated that there are some 45 years of “proven reserves,” thoughfuture oil demand will stress supplies. “Higher oil prices can retard economicgrowth and even cause a recession in the right circumstance,” Rusco told thebriefing. He declined to say after the briefing what a threshold gasoline
price might be for US consumers.
“The remaining hydrocarbons will be more costly to get from underground,” from a “policy perspective,” Rusco said, citing the Middle East.
Robert Hirsch, an energy adviser at MISI and former manager of
ExxonMobil’s synthetic fuels research laboratory, put the state of looming shortages in more dire terms, saying “in the next two to five years oil shortages will get deeper and deeper.”
Meanwhile, the “mitigation” of transitioning into other energy sources will take upward of a decade to come into play. “Some time after a decade, mitigation will take impact and things will start to flatten out” on the demand side, Hirsch said.
-Leslie Moore Mira, leslie_moore@platts.com