By Leslie Lang
The other day Richard gave some of us a tour of Hamakua Springs Country Farms in Pepe‘ekeo, and its new hydroelectric plant, and wow. I hadn’t been out to the farm for awhile, and it was so interesting to ride around the 600 acres with Richard and see all that’s going on there these days.
Most of what I realized (again) that afternoon fell into two
broad categories: That Richard really is a master of seeing the big picture, and that everything he does is related to that big picture.
Hamakua Springs, which started out growing bananas and then expanded into growing the deliciously sweet hydroponic tomatoes we all know the farm for, has other crops as well.

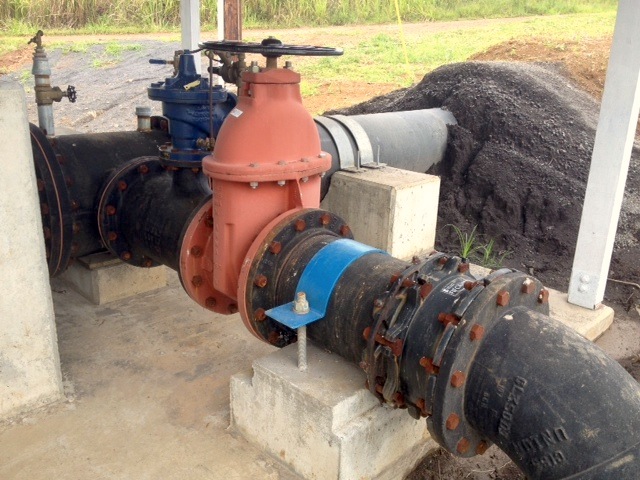
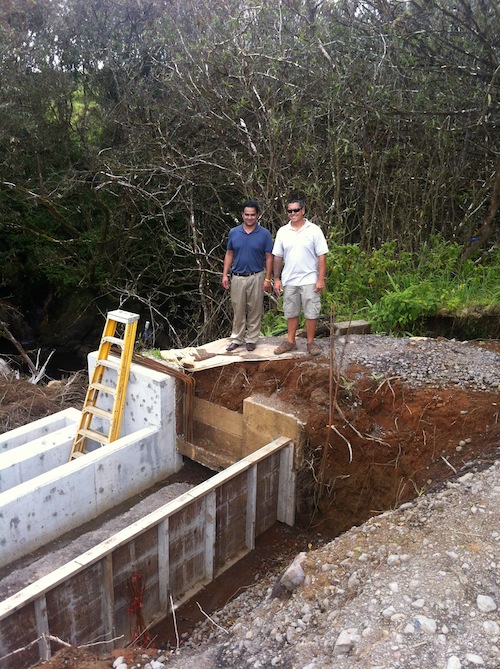
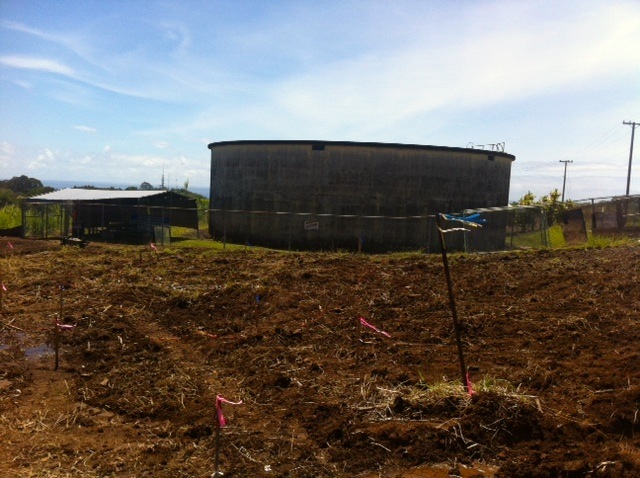
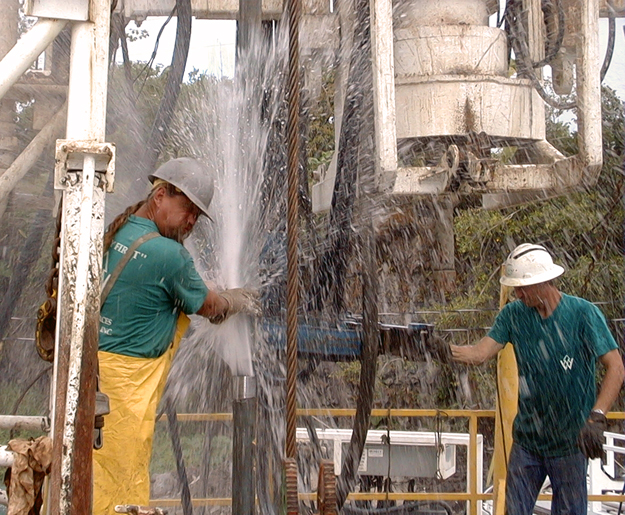
As we drove, we saw a lot of the water that passes through his farm. There are three streams and three springs. It’s an enormous amount of water, and it’s because of all this water that he was able to develop his brand new hydroelectric system, where they are getting ready to throw the switch.
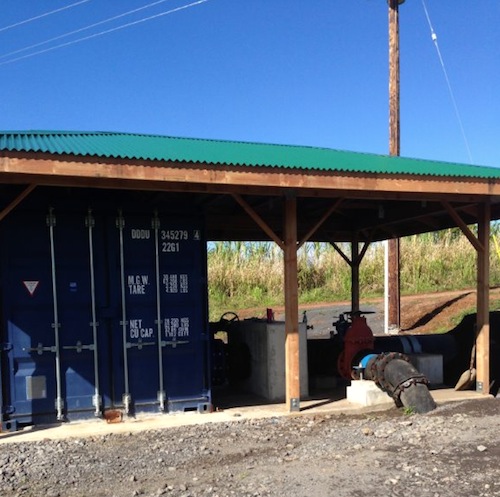
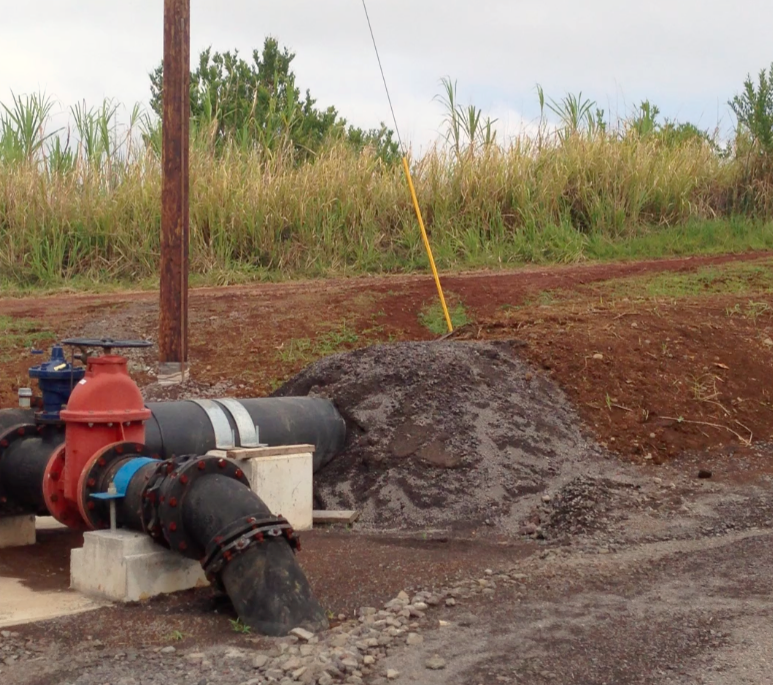
The water wasn’t running through there the day we were there because they’d had to temporarily “turn it off” – divert the water – in order to fix something, but we could see how the water from an old plantation flume now runs through the headworks and through a pipe and into the turbine, which is housed in a blue shipping container.
This is where the electricity is generated, and I was interested to see a lone electric pole standing there next to the system. End of the line! Or start of the line, really, as that’s where the electricity from the turbine is carried to. And from there, it works its way across the electric lines stretched between new poles reaching across the land.
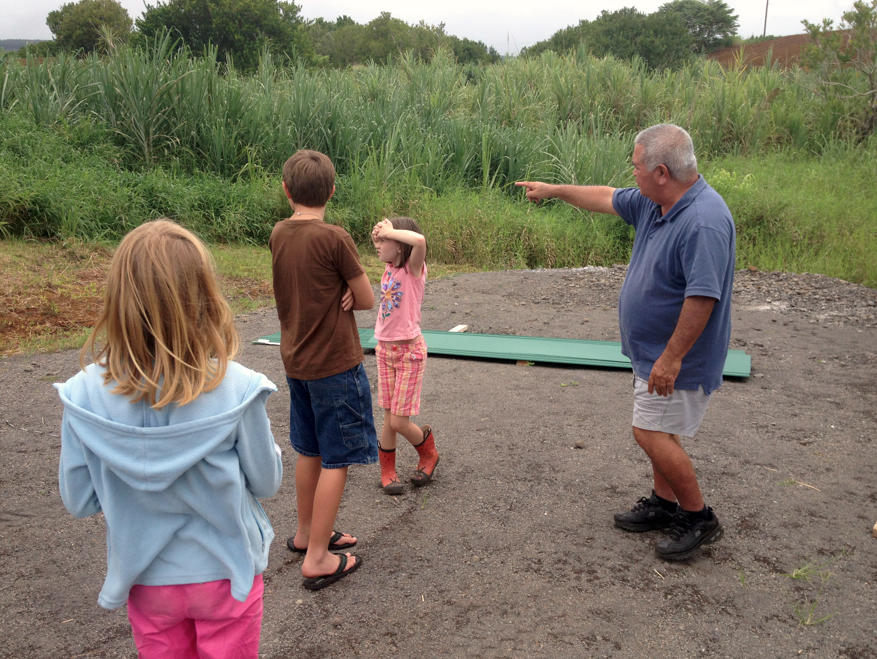
He asked the children who were along with us for their ideas
about how to landscape around the hydroelectric area, and also where the water leaves the turbine to run out and rejoin the stream.
“We could do anything here,” he said, asking for thoughts, and
we all came up with numerous ideas, some fanciful. Trees and grass? A taro lo‘i? Maybe a picnic area, or a water flume ride or a demonstration garden or fishponds?
There are interesting plans for once the hydro system is operating, including a certified kitchen where local area producers can bring their products and create value-added goods.
Other plans include having some sort of demo of sustainable
farming, and perhaps ag-tourism ativities like walking trails going through the farm, and maybe even a B&B. “The basis of all tourism,” he said, “is sustainability.”
Hamakua Springs is also experimenting with growing mushrooms
now, and looking into several other possibilities for using its free
electricity.
As we stopped and looked at the streams we kept coming
across, which ran under the old plantation roads we drove upon, Richard made an observation that I found interesting. In the Hawaiian way, the land is thought of as following the streams down from mountain to sea. In traditional ways, paths generally ran up-and-down the hill, following the shape of the ahupua‘a.
“But look at the plantation roads,” he said, and he pointed
out how they run across the land, from stream to stream. The plantation way was the opposite. Not “wrong” – just different.
Richard has plans to plant bamboo on the south sides of the
streams, which will keep the water cool and keep out invasive species.
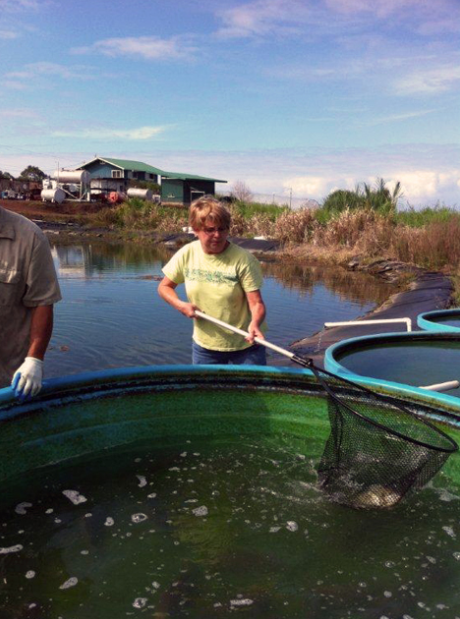
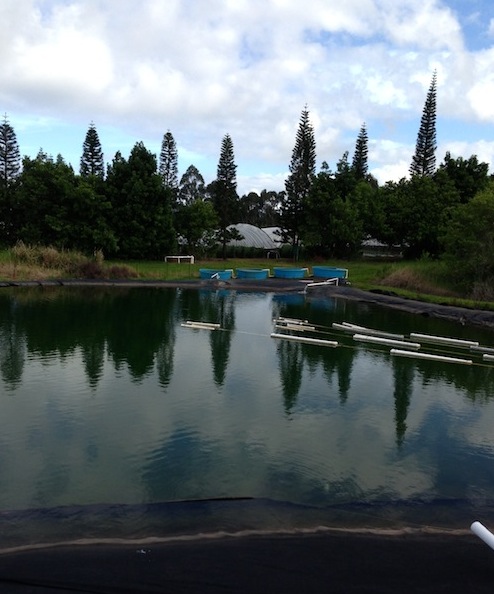
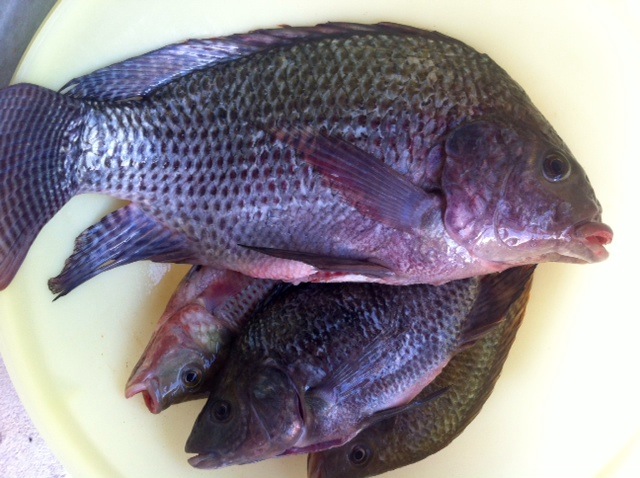
At the farm, they continue to experiment with raising
tilapia, which are in four blue pools next to the reservoir.
The pools are at different heights because they are using gravity to flow the water from one pool to the next, rather than a pump. Besides it being free, this oxygenates the water as it falls into the next pool. They are not raising the fish commercially at present, but give them to their workers.
Everything that Richard does is geared toward achieving the same goal, and that is to keep his farm economically viable and sustainable.
If farmers make money, farmers will farm.
Continuing to farm means continuing to provide food for the local community, employing people locally and making it possible for local people to stay in Hawai‘i: This as opposed to people having to leave the islands, or their children having to leave the islands, in order to make a decent life for themselves.
The hydroelectric system means saving thousands per month in
electric bills, and being able to expand into other products and activities. It means the farm stays in business and provides for the surrounding community. It means people have jobs.
This is the same reason why, on a bigger scale, Richard is working to bring more geothermal into the mix on the Big Island: to decrease the stranglehold that high electricity costs have over us, so the rubbah slippah folk have breathing room, so that we all have more disposable income – which will, in turn, drive our local economy and make our islands more competitive with the rest of the world, and our standard of living higher, comparably.
When he says “rubbah slippah folk,” Richard told me, he’s always thinking first about the farm’s workers.
This, by the way, is really a great overview of how Richard describes the “big picture.” It’s a TEDx talk he did awhile back (17 minutes). Really worth a look.
It was so interesting to see firsthand what is going on at the farm right now, and hear about the plans and the wheres and whyfors. Thank you, Richard, for a really interesting and insightful afternoon.