By guest blogger Rodrigo Romo:
With every question that seems to stir up controversy (geothermal, the Thirty Meter Telescope [TMT], etc.), the way I see it is to ask: "What would Kamehameha (or the old Hawaiians) do?"
The old Hawaiians lived in harmony with what the land/sea provided them, making sure they took care of their resources and making sure they were not depleted.
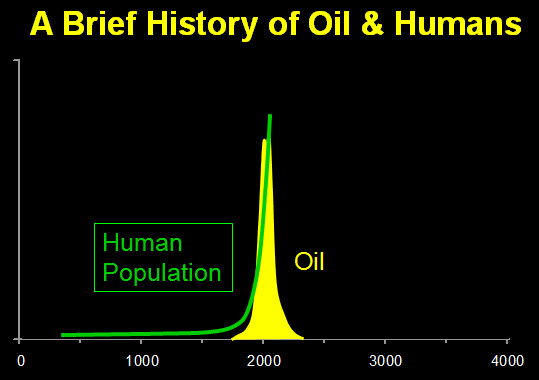
Would the old Hawaiians bring oil from distant lands to meet their energy needs? Or would they take advantage of what the land and the gods provided them (geothermal, solar, wind, hydroelectric)?
The old Hawaiians were famous for their star-based navigational skills. If they had the chance to further understand the universe from the top of Mauna Kea, would they pass on that opportunity? Or would they take advantage of the privileged location they were given by the land/gods to learn more about the universe?
I think part of the problem is that people underestimate what the old Hawaiians would do in today's technologically advanced world, and many think that they would still live like they did prior to the arrival of Cook.
I don't think that is the case. They were incredible wise people from an environmental point of view. They understood that by living on an island their resources were extremely limited and that their environment was very delicate.
Because of modern-day technology, we tend to forget that. It's easy for us to go to the grocery store and buy tomatoes from California, peaches from Chile and Atlantic salmon. We turn on the switch and expect the light to come on, because we know that there will be a ship/plane coming over to deliver our goods; goods that were not produced here from the land.
People see geothermal or wind as an intrusion to the environment, but have no problem with burning fossil fuels that are brought in from thousands of miles away.
They worry about the impact that a geothermal well may have on the air quality, but never think about the consequences that an oil spill from a tanker would have on our corals and the life around them.
People see the TMT as an intrusion into sacred land (regardless of the telescopes already present) but fail to see the wonderful opportunities it will provide to local young future Hawaiian scientists to be in the lead of space exploration.
We can learn a lot from the ways of the past: An understanding of the real value of our local resources, and how delicate our environment is. Combining that understanding with advances in technology will lead the path to achieving, or at least to moving closer to becoming a sustainable community/culture.
Aloha.
Rodrigo Romo was a member of the second Biosphere 2 crew. He is currently VP of Engineering for Zeta Corporation, where he is involved in water conservation projects. He lives in Hilo with his family.