In October 2008, the Hawai‘i Clean Energy Initiative (HCEI) – which aims for 70 percent of the State’s energy needs to be met by renewable energy by 2030 – was outstanding for its ambitious approach to the challenges facing Hawai‘i’s future. It anticipates a 30 percent reduction in oil dependency through efficiency improvements, plus a 2 percent/year reduction in fossil fuels over 20 years.
Now we are realizing that 40 percent less oil dependency in 20 years is not ambitious enough. And as we move to implementation, we are finding that some of our assumptions may not work out as planned. A key question is whether or not we are flexible enough to react to the rapid changes taking place.
It is clear to me that we are furiously sweeping and mopping the deck of the Titanic.

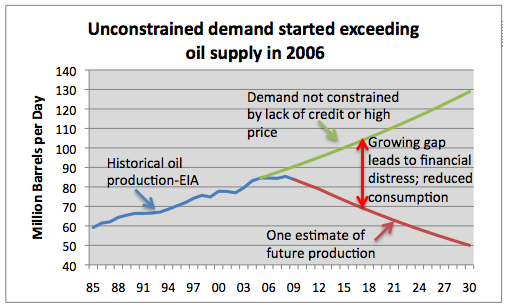
The Hawai‘i Clean Energy Initiative was enacted into law in April 2010. But by then, the world oil supply situation was changing rapidly. Two months later, Lloyd’s of London advised its business clients to be prepared for $200/barrel oil by the year 2013. Economists at the University of Hawai‘i Economic Research Organization told me that $200/barrel oil would devastate our tourist industry.
I asked, “Is it fair to say that if we used geothermal as our primary base power, Hawai‘i would become relatively more competitive to the rest of the world as the price of oil rises?” The answer was “yes.”
In a report last week, the Economic Research Organization at the University of Hawai‘I (UHERO) pointed out that the State’s current weak recovery is being fueled by the tourism industry—which is dependent on future oil prices.
Hawaii has liquid fuel, transportation and electricity problems. The mainland fixed its liquid fuel electricity problem, after the oil shocks of the 1970s, by switching to natural gas and coal.
This past October, when I attended a Peak Oil conference in Washington D.C., they pointed out that the U.S. mainland is less than 9 percent dependent on petroleum oil. A large part of that 9 percent, they then said, was due to the Hawaiian Electric Company (HECO) in Hawai‘i. I was shocked!
To think that we have done nothing about this for the last 20 years. And now we hear the excuse that, since nothing has been done, it will take 10 years to ramp up geothermal, so we cannot wait for geothermal.
Here is a comparison of Energy Return on Investment (EROI) for fossil fuels: In the 1930s, to get 100 barrels of oil, it took the energy of just one barrel. In the 1970s, one barrel would get you 30 barrels. Now, the average EROI is that one barrel will get you 10. Clearly, the trend is not good.
The ratio for geothermal is also around 10 to 1. The difference, though, is that this ratio will not decline for a very long time. Jim Kauahikaua, Scientist-in-Charge of the Hawaii Volcano Observatory, told me that the Big Island will be over the hot spot for 500,000 to a million years.
Instead of fossil fuel, HECO wants to use biofuels to generate the electricity for most of its base power. The problem is that the EROI for biofuels is close to 1 to 1. And it should also be a warning that SunFuels, a company that actually knows about green diesel, is closing up shop in Hawai‘i. Not to mention that farmers knew three years ago that they would not grow biofuels, because it was obviously a money loser for them.
I am not against biofuels, but I think if we are to grow liquid fuel it should be used for jet fuel or transportation fuel—not electricity. I support biofuels through Pacific Bioldiesel. These folks use waste oil to support their capital costs. To the extent they can integrate feedstock from farmers, I think that their model has a reasonable chance of success. I also support UH Hilo’s College of Agriculture and Forestry’s initiative to study palm oil cultivation. This, too, is proven technology.
Geothermal is cheap, proven, gives off no carbon emissions and occupies a very small footprint. And through the generation of NH3 from its off peak power, which can fuel internal combustion engines, geothermal can put future generations into a position so they can win.
NH3 can also help with food security. Eighty percent of NH3’s present use is as fertilizer.
Furthermore, electricity generated from geothermal to power electric cars is clean and cheap.
So geothermal both takes care of us today and can take care of future generations. To farmers, this is not rocket science. It’s just common sense.
We can and must use every renewable energy option available to us, and to its maximum potential. By diverting excess electricity production to alternatives such as NH3 (ammonia), geothermal offers a safety valve that can allow more renewable energy in.
Can we imagine prosperity, instead of doom and gloom? Not, no can. CAN!
The Hawaii Clean Energy Initiative:
On October 20, 2008, an Energy Agreement was signed by the State of Hawai’i, the Hawaiian Electric Companies, and the State Consumer Advocate to accelerate the accomplishment of Hawai’i’s energy objectives in the regulated electric utility sector.
In April, 2010, the Hawaii Clean Energy Initiative Program was added to State law, in Chapter 196 of the Hawaii Revised Statutes.
The Challenge
Hawai’i relies on imported petroleum for nearly 90% of its primary energy
Up to $7 billion flows out of the state annually to meet Hawai’i’s energy needs
Hawai’i’s economy is extremely vulnerable to fluctuations in global oil prices
Hawai’i residents pay among the nation’s highest prices for electricity and fuel
The Solution
The Hawai’i Clean Energy Initiative is helping transform Hawai’i from the most fossil-fuel dependent state in the nation to one run on Hawai’i Powered clean energy within a generation
Its goals and objectives:
Hawaii is the most fossil fuel dependent state in the nation.
This can be explained in large part because of our dependence on tourism and the military – together, they make up roughly 50% of our total economy. That’s a dangerous scenario for the future because of the finite nature of fossil fuel and the fact that our state is more and more vulnerable to fluctuations in oil prices and availability.